I created a MSN Group, CAD & Development MSN Group:
http://caddev.groups.live.com
We talk about CAD secondary development technology, e.g. UG/NX, ProE, AutoCAD, etc.
Welcome to join us!
2011-03-09
CAD & Development MSN Group
2011-03-03
Use CLR4 Hosting API to invoke .NET assembly from native C++ (Reprint)
The Common Language Runtime (CLR) allows a level of integration between itself and a host. This article is about a C++ code sample that demonstrates using the Hosting Interfaces of .NET Framework 4.0 to host a specific version of CLR in the process, load a .NET assembly, and invoke the types in the assembly. The code sample also demonstrates the new In-Process Side-by-Side feature in .NET Framework 4. The .NET Framework 4 runtime, and all future runtimes, are able to run in-process with one another. .NET Framework 4 runtime and beyond are also able to run in-process with any single older runtime. In ther words, you will be able to load 4, 5 and 2.0 in the same process, but you will not be able to load 1.1 and 2.0 in the same process. The code sample hosts .NET runtime 4.0 and 2.0 side by side, and loads a .NET 2.0 assembly into the two runtimes.
The code sample in this article (CppHostCLR) can be downloaded from Microsoft All-In-One Code Framework, which is a centralized code sample library.
The following steps walk through a demonstration of the CLR Hosting sample.
Step1. After you successfully build the sample project, and the dependent .NET class library projects (CSClassLibrary and CSNET2ClassLibrary) in Visual Studio 2010, you will get an application and two libraries: CppHostCLR.exe, CSClassLibrary.dll, and CSNET2ClassLibrary.dll. Make sure that the files are in the same folder.
Step2. Run the application in a command prompt. The application demonstrates the CLR In-Process Side-by-Side feature that is new in .NET 4 first. It hosts the .NET runtime 4.0 first and loads a .NET 2.0 assembly into the runtime to invoke its types. Then the application hosts the .NET runtime 2.0 side by side with the .NET runtime 4.0 and loads the same .NET 2.0 assembly into the .NET 4.0 runtime. If the operations succeed, the application prints the
following content in the console.
Load and start the .NET runtime v4.0.30319
Load the assembly CSNET2ClassLibrary
Call CSNET2ClassLibrary.CSSimpleObject.GetStringLength("HelloWorld") => 10
Call CSNET2ClassLibrary.CSSimpleObject.ToString() => 0.00
Load and start the .NET runtime v2.0.50727
Load the assembly CSNET2ClassLibrary
Call CSNET2ClassLibrary.CSSimpleObject.GetStringLength("HelloWorld") => 10
Call CSNET2ClassLibrary.CSSimpleObject.ToString() => 0.00
Presss ENTER to continue ...
You can verify that both .NET 2.0 and .NET 4.0 runtimes are loaded by using Process Explorer (http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb896653.aspx). In Lower Pane View / DLLs of the tool, you can see all modules loaded in the process. If clr.dll (the .NET 4 runtime module) and mscorwks.dll (the .NET 2 runtime module) are in the list, both .NET 2.0 and .NET 4.0 runtimes are loaded.
Step3. Press ENTER to continue. The application will host the .NET runtime 4.0 and use the ICLRRuntimeHost interface that was provided in .NET v2.0 to
load a .NET 4.0 assembly and invoke its type.
Load and start the .NET runtime v4.0.30319
Load the assembly CSClassLibrary.dll
Call CSClassLibrary.CSSimpleObject.GetStringLength("HelloWorld") => 10
The key code in the code sample is attached below.
1: // 2: // FUNCTION: RuntimeHostV4Demo1(PCWSTR, PCWSTR) 3: // 4: // PURPOSE: The function demonstrates using .NET Framework 4.0 Hosting 5: // Interfaces to host a .NET runtime, and use the ICorRuntimeHost interface 6: // that was provided in .NET v1.x to load a .NET assembly and invoke its 7: // type. 8: // 9: // If the .NET runtime specified by the pszVersion parameter cannot be 10: // loaded into the current process, the function prints ".NET runtime cannot be loaded", and return. 11: // 12: // If the .NET runtime is successfully loaded, the function loads the 13: // assembly identified by the pszAssemblyName parameter. Next, the function 14: // instantiates the class (pszClassName) in the assembly, calls its 15: // ToString() member method, and print the result. Last, the demo invokes 16: // the public static function 'int GetStringLength(string str)' of the class 17: // and print the result too. 18: // 19: // PARAMETERS: 20: // * pszVersion - The desired DOTNETFX version, in the format “°vX.X.XXXXX”±. 21: // The parameter must not be NULL. It’ˉs important to note that this 22: // parameter should match exactly the directory names for each version of 23: // the framework, under C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework[64]. The 24: // current possible values are "v1.0.3705", "v1.1.4322", "v2.0.50727" and 25: // "v4.0.30319". Also, note that the “°v”± prefix is mandatory. 26: // * pszAssemblyName - The display name of the assembly to be loaded, such 27: // as "CSClassLibrary". The ".DLL" file extension is not appended. 28: // * pszClassName - The name of the Type that defines the method to invoke. 29: // 30: // RETURN VALUE: HRESULT of the demo. 31: // 32: HRESULT RuntimeHostV4Demo1(PCWSTR pszVersion, PCWSTR pszAssemblyName, 33: PCWSTR pszClassName) 34: { 35: HRESULT hr; 36: ICLRMetaHost *pMetaHost = NULL; 37: ICLRRuntimeInfo *pRuntimeInfo = NULL; 38: // ICorRuntimeHost and ICLRRuntimeHost are the two CLR hosting interfaces 39: // supported by CLR 4.0. Here we demo the ICorRuntimeHost interface that 40: // was provided in .NET v1.x, and is compatible with all .NET Frameworks. 41: ICorRuntimeHost *pCorRuntimeHost = NULL; 42: IUnknownPtr spAppDomainThunk = NULL; 43: _AppDomainPtr spDefaultAppDomain = NULL; 44: // The .NET assembly to load. 45: bstr_t bstrAssemblyName(pszAssemblyName); 46: _AssemblyPtr spAssembly = NULL; 47: // The .NET class to instantiate. 48: bstr_t bstrClassName(pszClassName); 49: _TypePtr spType = NULL; 50: variant_t vtObject; 51: variant_t vtEmpty; 52: // The static method in the .NET class to invoke. 53: bstr_t bstrStaticMethodName(L"GetStringLength"); 54: SAFEARRAY *psaStaticMethodArgs = NULL; 55: variant_t vtStringArg(L"HelloWorld"); 56: variant_t vtLengthRet; 57: // The instance method in the .NET class to invoke. 58: bstr_t bstrMethodName(L"ToString"); 59: SAFEARRAY *psaMethodArgs = NULL; 60: variant_t vtStringRet; 61: // 62: // Load and start the .NET runtime. 63: // 64: wprintf(L"Load and start the .NET runtime %s \n", pszVersion); 65: hr = CLRCreateInstance(CLSID_CLRMetaHost, IID_PPV_ARGS(&pMetaHost)); 66: if (FAILED(hr)) 67: { 68: wprintf(L"CLRCreateInstance failed w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 69: goto Cleanup; 70: } 71: // Get the ICLRRuntimeInfo corresponding to a particular CLR version. It 72: // supersedes CorBindToRuntimeEx with STARTUP_LOADER_SAFEMODE. 73: hr = pMetaHost->GetRuntime(pszVersion, IID_PPV_ARGS(&pRuntimeInfo)); 74: if (FAILED(hr)) 75: { 76: wprintf(L"ICLRMetaHost::GetRuntime failed w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 77: goto Cleanup; 78: } 79: // Check if the specified runtime can be loaded into the process. This 80: // method will take into account other runtimes that may already be 81: // loaded into the process and set pbLoadable to TRUE if this runtime can 82: // be loaded in an in-process side-by-side fashion. 83: BOOL fLoadable; 84: hr = pRuntimeInfo->IsLoadable(&fLoadable); 85: if (FAILED(hr)) 86: { 87: wprintf(L"ICLRRuntimeInfo::IsLoadable failed w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 88: goto Cleanup; 89: } 90: if (!fLoadable) 91: { 92: wprintf(L".NET runtime %s cannot be loaded\n", pszVersion); 93: goto Cleanup; 94: } 95: // Load the CLR into the current process and return a runtime interface 96: // pointer. ICorRuntimeHost and ICLRRuntimeHost are the two CLR hosting 97: // interfaces supported by CLR 4.0. Here we demo the ICorRuntimeHost 98: // interface that was provided in .NET v1.x, and is compatible with all 99: // .NET Frameworks. 100: hr = pRuntimeInfo->GetInterface(CLSID_CorRuntimeHost, 101: IID_PPV_ARGS(&pCorRuntimeHost)); 102: if (FAILED(hr)) 103: { 104: wprintf(L"ICLRRuntimeInfo::GetInterface failed w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 105: goto Cleanup; 106: } 107: // Start the CLR. 108: hr = pCorRuntimeHost->Start(); 109: if (FAILED(hr)) 110: { 111: wprintf(L"CLR failed to start w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 112: goto Cleanup; 113: } 114: // 115: // Load the NET assembly. Call the static method GetStringLength of the 116: // class CSSimpleObject. Instantiate the class CSSimpleObject and call 117: // its instance method ToString. 118: // 119: // The following C++ code does the same thing as this C# code: 120: // 121: // Assembly assembly = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.Load(pszAssemblyName); 122: // object length = type.InvokeMember("GetStringLength", 123: // BindingFlags.InvokeMethod | BindingFlags.Static | 124: // BindingFlags.Public, null, null, new object[] { "HelloWorld" }); 125: // object obj = assembly.CreateInstance("CSClassLibrary.CSSimpleObject"); 126: // object str = type.InvokeMember("ToString", 127: // BindingFlags.InvokeMethod | BindingFlags.Instance | 128: // BindingFlags.Public, null, obj, new object[] { }); 129: // Get a pointer to the default AppDomain in the CLR. 130: hr = pCorRuntimeHost->GetDefaultDomain(&spAppDomainThunk); 131: if (FAILED(hr)) 132: { 133: wprintf(L"ICorRuntimeHost::GetDefaultDomain failed w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 134: goto Cleanup; 135: } 136: hr = spAppDomainThunk->QueryInterface(IID_PPV_ARGS(&spDefaultAppDomain)); 137: if (FAILED(hr)) 138: { 139: wprintf(L"Failed to get default AppDomain w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 140: goto Cleanup; 141: } 142: // Load the .NET assembly. 143: wprintf(L"Load the assembly %s\n", pszAssemblyName); 144: hr = spDefaultAppDomain->Load_2(bstrAssemblyName, &spAssembly); 145: if (FAILED(hr)) 146: { 147: wprintf(L"Failed to load the assembly w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 148: goto Cleanup; 149: } 150: // Get the Type of CSSimpleObject. 151: hr = spAssembly->GetType_2(bstrClassName, &spType); 152: if (FAILED(hr)) 153: { 154: wprintf(L"Failed to get the Type interface w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 155: goto Cleanup; 156: } 157: // Call the static method of the class: 158: // public static int GetStringLength(string str); 159: // Create a safe array to contain the arguments of the method. The safe 160: // array must be created with vt = VT_VARIANT because .NET reflection 161: // expects an array of Object - VT_VARIANT. There is only one argument, 162: // so cElements = 1. 163: psaStaticMethodArgs = SafeArrayCreateVector(VT_VARIANT, 0, 1); 164: LONG index = 0; 165: hr = SafeArrayPutElement(psaStaticMethodArgs, &index, &vtStringArg); 166: if (FAILED(hr)) 167: { 168: wprintf(L"SafeArrayPutElement failed w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 169: goto Cleanup; 170: } 171: // Invoke the "GetStringLength" method from the Type interface. 172: hr = spType->InvokeMember_3(bstrStaticMethodName, static_cast( 173: BindingFlags_InvokeMethod | BindingFlags_Static | BindingFlags_Public), 174: NULL, vtEmpty, psaStaticMethodArgs, &vtLengthRet); 175: if (FAILED(hr)) 176: { 177: wprintf(L"Failed to invoke GetStringLength w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 178: goto Cleanup; 179: } 180: // Print the call result of the static method. 181: wprintf(L"Call %s.%s(\"%s\") => %d\n", 182: static_cast(bstrClassName), 183: static_cast(bstrStaticMethodName), 184: static_cast(vtStringArg.bstrVal), 185: vtLengthRet.lVal); 186: // Instantiate the class. 187: hr = spAssembly->CreateInstance(bstrClassName, &vtObject); 188: if (FAILED(hr)) 189: { 190: wprintf(L"Assembly::CreateInstance failed w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 191: goto Cleanup; 192: } 193: // Call the instance method of the class. 194: // public string ToString(); 195: // Create a safe array to contain the arguments of the method. 196: psaMethodArgs = SafeArrayCreateVector(VT_VARIANT, 0, 0); 197: // Invoke the "ToString" method from the Type interface. 198: hr = spType->InvokeMember_3(bstrMethodName, static_cast( 199: BindingFlags_InvokeMethod | BindingFlags_Instance | BindingFlags_Public), 200: NULL, vtObject, psaMethodArgs, &vtStringRet); 201: if (FAILED(hr)) 202: { 203: wprintf(L"Failed to invoke ToString w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 204: goto Cleanup; 205: } 206: // Print the call result of the method. 207: wprintf(L"Call %s.%s() => %s\n", 208: static_cast(bstrClassName), 209: static_cast(bstrMethodName), 210: static_cast(vtStringRet.bstrVal)); 211: Cleanup: 212: if (pMetaHost) 213: { 214: pMetaHost->Release(); 215: pMetaHost = NULL; 216: } 217: if (pRuntimeInfo) 218: { 219: pRuntimeInfo->Release(); 220: pRuntimeInfo = NULL; 221: } 222: if (pCorRuntimeHost) 223: { 224: // Please note that after a call to Stop, the CLR cannot be 225: // reinitialized into the same process. This step is usually not 226: // necessary. You can leave the .NET runtime loaded in your process. 227: //wprintf(L"Stop the .NET runtime\n"); 228: //pCorRuntimeHost->Stop(); 229: pCorRuntimeHost->Release(); 230: pCorRuntimeHost = NULL; 231: } 232: if (psaStaticMethodArgs) 233: { 234: SafeArrayDestroy(psaStaticMethodArgs); 235: psaStaticMethodArgs = NULL; 236: } 237: if (psaMethodArgs) 238: { 239: SafeArrayDestroy(psaMethodArgs); 240: psaMethodArgs = NULL; 241: } 242: return hr; 243: } 244: 245: // 246: // FUNCTION: RuntimeHostV4Demo2(PCWSTR, PCWSTR) 247: // 248: // PURPOSE: The function demonstrates using .NET Framework 4.0 Hosting 249: // Interfaces to host a .NET runtime, and use the ICLRRuntimeHost interface 250: // that was provided in .NET v2.0 to load a .NET assembly and invoke its 251: // type. Because ICLRRuntimeHost is not compatible with .NET runtime v1.x, 252: // the requested runtime must not be v1.x. 253: // 254: // If the .NET runtime specified by the pszVersion parameter cannot be 255: // loaded into the current process, the function prints ".NET runtime cannot be loaded", and return. 256: // 257: // If the .NET runtime is successfully loaded, the function loads the 258: // assembly identified by the pszAssemblyName parameter. Next, the function 259: // invokes the public static function 'int GetStringLength(string str)' of 260: // the class and print the result. 261: // 262: // PARAMETERS: 263: // * pszVersion - The desired DOTNETFX version, in the format “°vX.X.XXXXX”±. 264: // The parameter must not be NULL. It’ˉs important to note that this 265: // parameter should match exactly the directory names for each version of 266: // the framework, under C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework[64]. Because 267: // the ICLRRuntimeHost interface does not support the .NET v1.x runtimes, 268: // the current possible values of the parameter are "v2.0.50727" and 269: // "v4.0.30319". Also, note that the “°v”± prefix is mandatory. 270: // * pszAssemblyPath - The path to the Assembly to be loaded. 271: // * pszClassName - The name of the Type that defines the method to invoke. 272: // 273: // RETURN VALUE: HRESULT of the demo. 274: // 275: HRESULT RuntimeHostV4Demo2(PCWSTR pszVersion, PCWSTR pszAssemblyPath, 276: PCWSTR pszClassName) 277: { 278: HRESULT hr; 279: ICLRMetaHost *pMetaHost = NULL; 280: ICLRRuntimeInfo *pRuntimeInfo = NULL; 281: // ICorRuntimeHost and ICLRRuntimeHost are the two CLR hosting interfaces 282: // supported by CLR 4.0. Here we demo the ICLRRuntimeHost interface that 283: // was provided in .NET v2.0 to support CLR 2.0 new features. 284: // ICLRRuntimeHost does not support loading the .NET v1.x runtimes. 285: ICLRRuntimeHost *pClrRuntimeHost = NULL; 286: // The static method in the .NET class to invoke. 287: PCWSTR pszStaticMethodName = L"GetStringLength"; 288: PCWSTR pszStringArg = L"HelloWorld"; 289: DWORD dwLengthRet; 290: // 291: // Load and start the .NET runtime. 292: // 293: wprintf(L"Load and start the .NET runtime %s \n", pszVersion); 294: hr = CLRCreateInstance(CLSID_CLRMetaHost, IID_PPV_ARGS(&pMetaHost)); 295: if (FAILED(hr)) 296: { 297: wprintf(L"CLRCreateInstance failed w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 298: goto Cleanup; 299: } 300: // Get the ICLRRuntimeInfo corresponding to a particular CLR version. It 301: // supersedes CorBindToRuntimeEx with STARTUP_LOADER_SAFEMODE. 302: hr = pMetaHost->GetRuntime(pszVersion, IID_PPV_ARGS(&pRuntimeInfo)); 303: if (FAILED(hr)) 304: { 305: wprintf(L"ICLRMetaHost::GetRuntime failed w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 306: goto Cleanup; 307: } 308: // Check if the specified runtime can be loaded into the process. This 309: // method will take into account other runtimes that may already be 310: // loaded into the process and set pbLoadable to TRUE if this runtime can 311: // be loaded in an in-process side-by-side fashion. 312: BOOL fLoadable; 313: hr = pRuntimeInfo->IsLoadable(&fLoadable); 314: if (FAILED(hr)) 315: { 316: wprintf(L"ICLRRuntimeInfo::IsLoadable failed w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 317: goto Cleanup; 318: } 319: if (!fLoadable) 320: { 321: wprintf(L".NET runtime %s cannot be loaded\n", pszVersion); 322: goto Cleanup; 323: } 324: // Load the CLR into the current process and return a runtime interface 325: // pointer. ICorRuntimeHost and ICLRRuntimeHost are the two CLR hosting 326: // interfaces supported by CLR 4.0. Here we demo the ICLRRuntimeHost 327: // interface that was provided in .NET v2.0 to support CLR 2.0 new 328: // features. ICLRRuntimeHost does not support loading the .NET v1.x 329: // runtimes. 330: hr = pRuntimeInfo->GetInterface(CLSID_CLRRuntimeHost, 331: IID_PPV_ARGS(&pClrRuntimeHost)); 332: if (FAILED(hr)) 333: { 334: wprintf(L"ICLRRuntimeInfo::GetInterface failed w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 335: goto Cleanup; 336: } 337: // Start the CLR. 338: hr = pClrRuntimeHost->Start(); 339: if (FAILED(hr)) 340: { 341: wprintf(L"CLR failed to start w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 342: goto Cleanup; 343: } 344: // 345: // Load the NET assembly and call the static method GetStringLength of 346: // the type CSSimpleObject in the assembly. 347: // 348: wprintf(L"Load the assembly %s\n", pszAssemblyPath); 349: // The invoked method of ExecuteInDefaultAppDomain must have the 350: // following signature: static int pwzMethodName (String pwzArgument) 351: // where pwzMethodName represents the name of the invoked method, and 352: // pwzArgument represents the string value passed as a parameter to that 353: // method. If the HRESULT return value of ExecuteInDefaultAppDomain is 354: // set to S_OK, pReturnValue is set to the integer value returned by the 355: // invoked method. Otherwise, pReturnValue is not set. 356: hr = pClrRuntimeHost->ExecuteInDefaultAppDomain(pszAssemblyPath, 357: pszClassName, pszStaticMethodName, pszStringArg, &dwLengthRet); 358: if (FAILED(hr)) 359: { 360: wprintf(L"Failed to call GetStringLength w/hr 0x%08lx\n", hr); 361: goto Cleanup; 362: } 363: // Print the call result of the static method. 364: wprintf(L"Call %s.%s(\"%s\") => %d\n", pszClassName, pszStaticMethodName, 365: pszStringArg, dwLengthRet); 366: Cleanup: 367: if (pMetaHost) 368: { 369: pMetaHost->Release(); 370: pMetaHost = NULL; 371: } 372: if (pRuntimeInfo) 373: { 374: pRuntimeInfo->Release(); 375: pRuntimeInfo = NULL; 376: } 377: if (pClrRuntimeHost) 378: { 379: // Please note that after a call to Stop, the CLR cannot be 380: // reinitialized into the same process. This step is usually not 381: // necessary. You can leave the .NET runtime loaded in your process. 382: //wprintf(L"Stop the .NET runtime\n"); 383: //pClrRuntimeHost->Stop(); 384: pClrRuntimeHost->Release(); 385: pClrRuntimeHost = NULL; 386: } 387: return hr; 388: }Original post:http://blogs.msdn.com/b/msdnforum/archive/2010/07/09/use-clr4-hosting-api-to-invoke-net-assembly-from-native-c.aspx
I realiezed the second function in MFC console, nor the other.
The mechanism of UG/NX Load .net dll
Now we talk about how UG/NX load a .net plugin dll.
As far as we know, NX run without .net framework, i.e., no need setup .net framework on the PC to use NX.
But, why NX can also load .net dll. (Of cource, who use .net plugin should setup .net framework by selves).
As I known, a native C/C++ program to load a .net program could use CLI, COM, and API methods. Others are between processes.
Obviously, NX didn't use CLI nor COM, because of both methods should prepare .net framework on PC.
API is the short of CLR Hodting APIs, some COM components to load .net program.
API is different with .net versions, especially .net4 having in process side by side which let it be reprogram. (The usage of .net API is not the businee of this post and I would post another article latter).
Conclusion, NX load the customer .net dll with ManagedLoader.dll by .net hosing API.
ManagedLoader.dll is a key component.
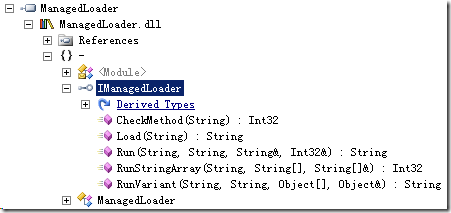
Let us have a look for it.
From the Fig., we see a interface and a class which is a implementation of the former.
The interface realiezed how to load a .net dll, and run their methods.
We pay attension to Load(string), for it is take charge for loading the customer dll. So, let's look:
1: public string Load(string assemblyName)
2: {3: string str = null;
4: this.myAssemblyName = assemblyName;
5: Trace.WriteLine(string.Concat(new object[] { "ManagedLoader.Load: ", assemblyName, " ", AppDomain.CurrentDomain }));
6: Trace.WriteLine("AppBase: " + AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory);
7: try
8: {9: AppDomain.CurrentDomain.AssemblyResolve += new ResolveEventHandler(this.AssemblyResolveHandler);
10: AppDomain.CurrentDomain.AssemblyLoad += new AssemblyLoadEventHandler(this.AssemblyLoadHandler);
11: this.myAssembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(assemblyName);
12: }13: catch (Exception exception)
14: { 15: Trace.WriteLine(exception.ToString()); 16: str = exception.ToString(); 17: }18: return str;
19: } 20: 21: Line 9, mainly correspond to loading dll successfully event. There is nothing, only Trace information for debugging.
Line 10, deal with loading the dependent dlls, very importantly, details latter.
Line 11, load customer .net dll. Note, it use LoadForm, not LoadFile, there is differen between them.
In addition, reflection have some variation in .net4, you could look for MSDN.
What are dependent dlls?
Different from native dlls which could be found form the Path directory. .net dll only could put donw in exe path or GAC.
That's the problem. The main process of UG/NX is ugraf.exe, at program files/UGS… . It could not ask put all customer dlls in there, so there must be some place for users.
Except the path of the customer dll, NX allows the path speciafied by the system variable UGII_MANAGED_DLL_PATH to put down.
The Event AssemblyResolve deal with searching these dependent dlls, you can look:http://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/system.appdomain.assemblyresolve(v=vs.80).aspx
Now, let's see the implementation of above line 10 function.
1: private Assembly AssemblyResolveHandler(object sender, ResolveEventArgs args)
2: {3: Trace.WriteLine("Resolve failed: " + args.Name);
4: int index = args.Name.IndexOf(',');
5: string str = args.Name.Substring(0, index);
6: if ((!(str == "NXOpen") && !(str == "NXOpen.Utilities")) && (!(str == "NXOpenUI") && !(str == "NXOpen.UF")))
7: {8: return null;
9: }10: str = str + ".dll";
11: string str2 = TranslateVariable("UGII_MANAGED_DLL_PATH");
12: string path = null;
13: if (str2 != null)
14: {15: foreach (string str4 in str2.Split(new char[] { Path.PathSeparator }))
16: { 17: path = Path.Combine(str4, str);18: if (File.Exists(path))
19: {20: break;
21: }22: path = null;
23: } 24: }25: if (path == null)
26: {27: str2 = TranslateVariable("UGII_ROOT_DIR");
28: if (str2 != null)
29: {30: path = Path.Combine(Path.Combine(str2, "managed"), str);
31: } 32: } 33: Assembly assembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(path);34: if (assembly == null)
35: {36: Trace.WriteLine("Failed to load: " + str);
37: return assembly;
38: }39: Trace.WriteLine("Loaded: : " + assembly.GetName(false).ToString());
40: return assembly;
41: }4-5, acquire the name of a dependent dll.
6-9, exclude 4 dlls laoding automatically with ManagedLoader.dll.
10-24, search them in the path speciafied by UGII_MANAGED_DLL_PATH.
25-32, search them in the path specialfied by UGII_ROOR_DIR which is the root of UG/NX.
Line 33, load the dependent dll.
34-38, deal with errors.
Ohters are searched form the path of the customer plugin, which is automatically realized by reflection of .net.
OK, that's all.
About .net API usage, we talk about latter.
All rights 白途思(Beck)
2011-03-01